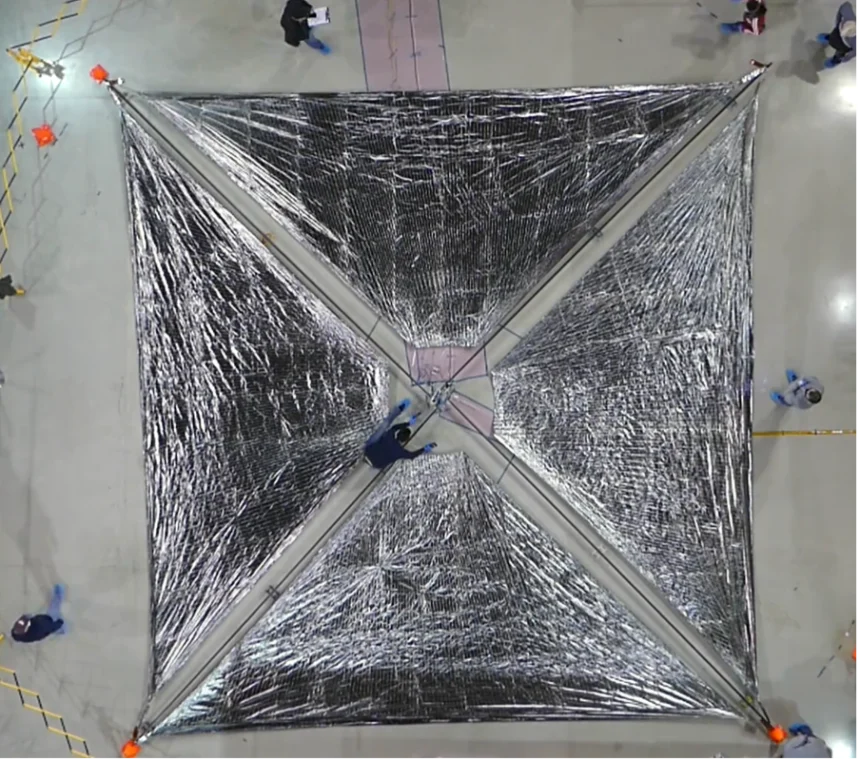
In a remarkable technological achievement, NASA has successfully deployed a vast solar sail the size of a basketball court. This experimental spacecraft propulsion system could usher in a new era of deep space exploration, using the sun’s radiation for fuel-free space travel.
What is a Solar Sail?
Solar sails are large, ultra-thin reflective membranes. Unlike traditional spacecrafts propelled by chemical fuels, they harness the continuous pressure of sunlight photons. While this pressure is very slight, it accumulates over time, steadily increasing the spacecraft’s velocity.
NASA’s Advanced Composite Solar Sail System (ACS3)
This latest demonstration from NASA showcases a significant improvement on previous solar sail designs. The ACS3 is composed of a polymer material coated with aluminum, achieving unmatched lightness with outstanding reflective capability. Additionally, it utilizes four lightweight and durable booms to stretch the sail out to its full span.
Advantages of Solar Sailing
- Fuel-free Navigation: Solar sails enable continuous acceleration without the burden of heavy fuel tanks, allowing for longer and further space missions.
- Uncharted Destinations: Without requiring traditional fuel refills, solar sail probes can reach areas of the solar system too distant for conventional spacecraft.
- Cost-Effectiveness: In the long run, solar sail technology can drastically reduce the costs associated with payload launches and complex maneuvering systems.
Recent Success and Future Potential
This recent test paves the way for even larger solar sails to support ambitious missions. Potential applications include:
- Solar System Exploration: Studying the sun’s activity up close, reaching less accessible asteroids or the outer planets of our solar system.
- Space Communication: Solar sail crafts could act as large relays, expanding interplanetary communication networks.
- Earth Defense: Potential as giant mirrors to redirect space debris or as early warning detectors of threats emanating from the sun.
Challenges and Limitations
- Slow Initial Acceleration: Acceleration for solar sails is gradual, and maneuvers can be time-consuming.
- Dependence on the Sun: Efficiency decreases as a solar sail navigates further from the sun.
The Expanding Universe of Space Exploration
NASA’s success with the ACS3 marks another landmark in our understanding and utilization of spacefaring technology. While solar sails may not entirely replace chemical propulsion systems, they are proving their utility and versatility. The potential for these giant, sunlight-powered vessels brings the promise of exciting future missions as we push the boundaries of how we explore our universe.