A paradigm shift is currently occurring in the medical field due to the introduction of bio-imaging libraries, which represent an innovative strategy for the timely identification of malignancies. Bio-imaging banks, which serve as repositories for medical images, are revolutionizing cancer diagnosis and treatment through the utilization of sophisticated imaging technology and data analytics. The implications of bio-imaging repositories facilitating early cancer detection for the future of healthcare are discussed in this article.
1. The Inception of Bio-Imaging Banks
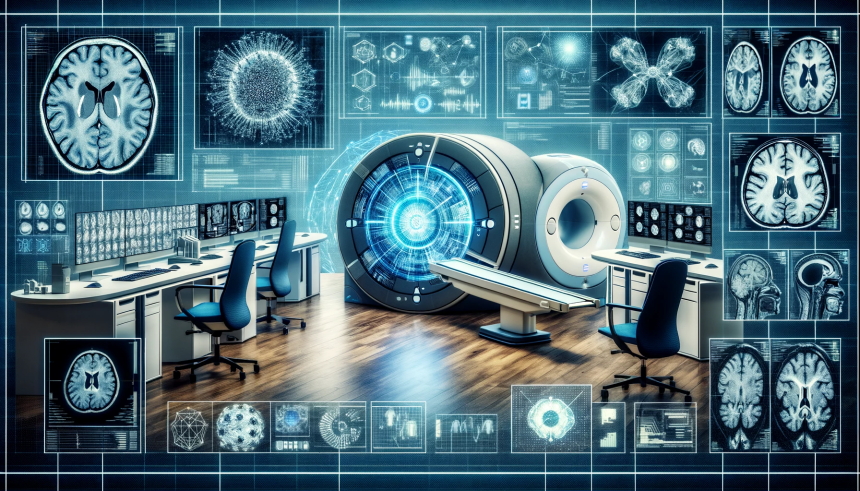
Centralized databases containing a vast assortment of medical images, including X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, are known as bio-imaging banks. These repositories serve a purpose beyond mere storage; they function as dynamic resources that facilitate the analysis of medical images in order to detect patterns and markers that are suggestive of cancer in its early stages.
2. Sophisticated Imaging Technologies
Bio-imaging institutions are founded upon cutting-edge imaging technology. Particle emission tomography (PET), computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are methods that generate intricate visual representations of the internal structures of the body. These images provide invaluable information for monitoring changes in organs and tissues over time, which may indicate the initiation of cancer.
3. Application of AI and ML to Image Analysis
The actual efficacy of bio-imaging libraries resides in their implementation of machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence (AI). These technologies have the capability to analyze extensive collections of medical images, detecting nuanced alterations and patterns that may elude the human eye. In order to identify early indications of cancer, frequently well in advance of the onset of symptoms or conventional diagnostic techniques, AI algorithms are programmed to do so.
4. Prompt Identification of Cancer
Early detection of cancer is vital in the fight against the disease. Detection of cancer at an earlier stage increases the likelihood of effective treatment and survival. Early detection is facilitated by bio-imaging libraries, which provide longitudinal, detailed medical images that may unveil the earliest indications of malignant transformations.
5. Predictive Analysis and Personalized Medicine
The utilization of bio-imaging repositories substantially advances personalized medicine. Through the examination of an individual’s imaging history, medical professionals are able to develop individualized surveillance and treatment strategies. Additionally, individuals who are at a greater risk can be identified through predictive analysis, enabling proactive monitoring and early intervention.
6. Obstacles and Ethical Determinations
Although bio-imaging institutions exhibit significant potential, they also pose certain obstacles. Ensuring data privacy and security is of the utmost importance, given that these financial institutions hold sensitive personal health information. It is imperative to thoroughly address ethical considerations pertaining to data usage, consent, and patient confidentiality.
7. Collaborative Research and Efforts
Bio-imaging banks frequently function as components of more extensive collaborative research endeavors that encompass technology corporations, research institutions, and hospitals. These partnerships are crucial for the progression of cancer research, the enhancement of imaging technologies, and the optimization of AI algorithms.
In conclusion,
Bio-imaging repositories signify a substantial advancement in the field of cancer treatment and diagnosis. They offer the possibility of enhanced patient outcomes by facilitating early cancer detection via sophisticated imaging and AI analysis. With the ongoing advancements in technology and research, it is highly probable that bio-imaging institutions will emerge as a critical component of healthcare, fundamentally altering the domains of cancer detection and personalized medicine.